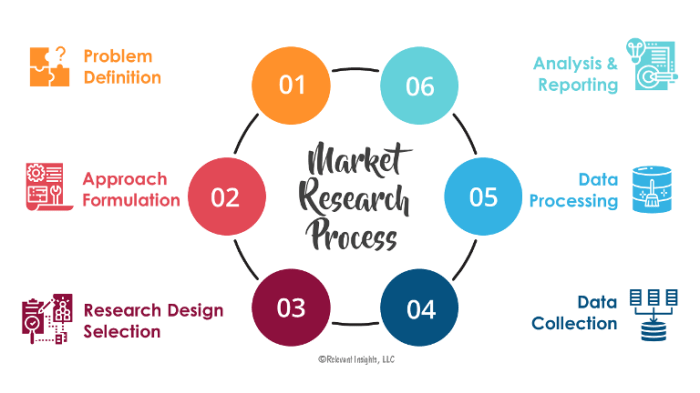
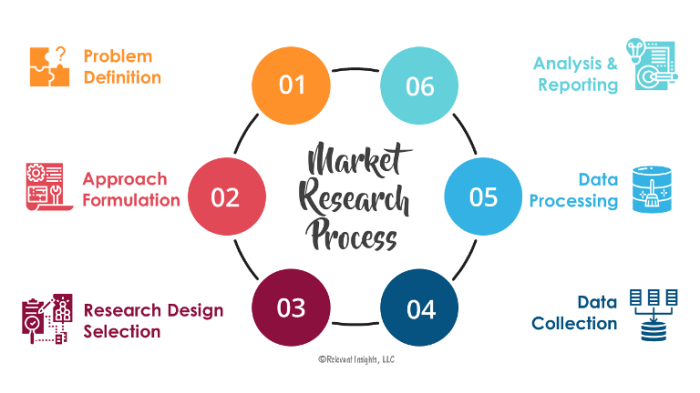
Building a Marketing Research Process sets the foundation for successful decision-making in companies by outlining key steps and strategies. Dive into the world of structured research to unlock valuable insights and drive business growth.
Overview of Marketing Research Process
Marketing research is crucial for companies to understand their target market, competition, and industry trends. Building a structured marketing research process helps businesses make informed decisions based on data-driven insights. By following key steps in creating an effective marketing research process, companies can gather valuable information to guide their strategies and improve their overall performance.
Identifying Research Objectives
- Define clear research objectives to focus on specific goals and outcomes.
- Establish criteria for success to measure the effectiveness of the research process.
Data Collection and Analysis
- Gather data through various methods such as surveys, interviews, and observations.
- Analyze the collected data to extract meaningful insights and trends.
Market Segmentation and Targeting
- Segment the market based on demographics, psychographics, and behavioral factors.
- Identify target segments to tailor marketing strategies and messages effectively.
Competitive Analysis
- Evaluate competitors’ strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to identify market opportunities.
- Develop strategies to differentiate the company from competitors and gain a competitive advantage.
Decision Making and Implementation
- Utilize research findings to make informed decisions on product development, pricing, promotion, and distribution.
- Implement marketing strategies based on research insights to achieve business objectives.
Defining Research Objectives
In the marketing research process, defining research objectives is crucial for guiding the study in the right direction and ensuring the desired outcomes are achieved. Clear research objectives help in focusing efforts, resources, and time effectively.
Significance of Clearly Defined Research Objectives
Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) research objectives is essential for ensuring the success of a marketing research study. By following the SMART criteria, researchers can establish clear goals and parameters for their research, which helps in maintaining focus and measuring progress accurately.
- Specific: Objectives should be well-defined and precise, outlining exactly what needs to be achieved.
- Measurable: Objectives should include metrics that can be used to evaluate the success of the research study.
- Achievable: Objectives should be realistic and attainable within the resources and constraints of the study.
- Relevant: Objectives should be directly related to the research problem and provide meaningful insights for decision-making.
- Time-bound: Objectives should have a clear timeline for completion, ensuring that the research study stays on track.
Impact of Vague Research Objectives, Building a Marketing Research Process
When research objectives are vague or poorly defined, it can lead to several negative outcomes in a marketing research study. Vague objectives may result in confusion, lack of direction, and misalignment with the overall research goals. This can lead to wasted resources, inaccurate data collection, and ultimately, unreliable results that do not address the research problem effectively.
Setting clear and SMART research objectives is essential for ensuring the success and credibility of a marketing research study.
Research Design and Methodology
Research design plays a crucial role in shaping the marketing research process by providing a framework for collecting and analyzing data to address specific research objectives. It Artikels the overall plan that guides researchers in conducting their study effectively and efficiently.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Approaches
- Qualitative research focuses on understanding behaviors, attitudes, and motivations through in-depth interviews, focus groups, or observations. It provides rich, detailed insights but may not be easily generalizable.
- Quantitative research, on the other hand, involves numerical data and statistical analysis to quantify relationships and patterns. It allows for broader generalizations but may lack the depth of qualitative insights.
Choosing the right research methodology depends on the research objectives and the type of information needed to answer the research questions effectively.
Reliability and Validity of Research Findings
- Reliability refers to the consistency and repeatability of research findings. A well-designed research study should produce consistent results when conducted multiple times.
- Validity, on the other hand, relates to the accuracy and truthfulness of the research findings. It ensures that the study measures what it intends to measure and that the results are meaningful and applicable.
Data Collection Techniques
In marketing research, data collection techniques play a crucial role in gathering valuable insights to make informed decisions. Various methods are commonly used, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. It is essential to select the most appropriate technique based on the research objectives to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data collected.
Surveys
Surveys are one of the most popular data collection techniques in marketing research. They involve asking a series of questions to a sample of individuals to gather their opinions, preferences, and feedback. Surveys can be conducted through online forms, telephone interviews, or face-to-face interactions.
- Advantages:
- Reach a large audience quickly.
- Collect quantitative data for analysis.
- Cost-effective compared to other methods.
- Disadvantages:
- Potential for response bias.
- Limited depth of responses compared to qualitative methods.
- Low response rates in some cases.
Focus Groups
Focus groups involve gathering a small group of individuals to discuss specific topics in a structured setting. This technique allows researchers to observe group dynamics and interactions to gain insights into consumer behaviors, attitudes, and perceptions.
- Advantages:
- Facilitate in-depth discussions and insights.
- Generate qualitative data for analysis.
- Encourage brainstorming and idea generation.
- Disadvantages:
- Group dynamics can influence responses.
- Costly and time-consuming to organize.
- Results may not be generalizable to the larger population.
Interviews
Interviews involve one-on-one interactions between a researcher and a respondent to gather detailed information on specific topics. This method allows for probing questions, clarification, and deeper insights into individual opinions and experiences.
- Advantages:
- Personalized approach to data collection.
- Opportunity for in-depth exploration of topics.
- Flexibility to adapt questions based on responses.
- Disadvantages:
- Time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Potential for interviewer bias.
- Difficulty in ensuring consistency across interviews.
Observation
Observation involves directly watching and recording behaviors, interactions, and activities of individuals or groups in real-life settings. This method allows researchers to gather data without relying on self-reported information from respondents.
- Advantages:
- Provides firsthand data on actual behaviors.
- Less reliance on respondent memory or bias.
- Useful for studying non-verbal cues and actions.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited ability to probe for explanations.
- Difficulty in interpreting certain behaviors.
- Time-consuming and may require trained observers.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Data analysis and interpretation are crucial steps in the marketing research process as they help in making informed decisions based on the collected data. By using statistical tools, software, and techniques, researchers can uncover patterns, trends, and relationships within the data to draw meaningful insights for marketing strategies.
Utilizing Statistical Tools and Software
- Statistical tools like SPSS, SAS, or R are commonly used to analyze quantitative data and generate reports.
- Data visualization software such as Tableau or Power BI can help in creating interactive dashboards to present findings effectively.
Techniques for Data Analysis
- Descriptive analysis involves summarizing data using measures like mean, median, and mode to gain a better understanding of the data.
- Inferential analysis helps in making predictions or generalizations about a population based on a sample data set.
- Regression analysis can be used to identify relationships between variables and predict future outcomes.
Drawing Insights for Marketing Strategies
- Segmentation analysis can help in identifying target market segments based on demographic, psychographic, or behavioral characteristics.
- Conjoint analysis can assist in determining the most preferred product features or pricing strategies among consumers.
- Sentiment analysis of social media data can provide insights into customer perceptions and preferences regarding a brand or product.
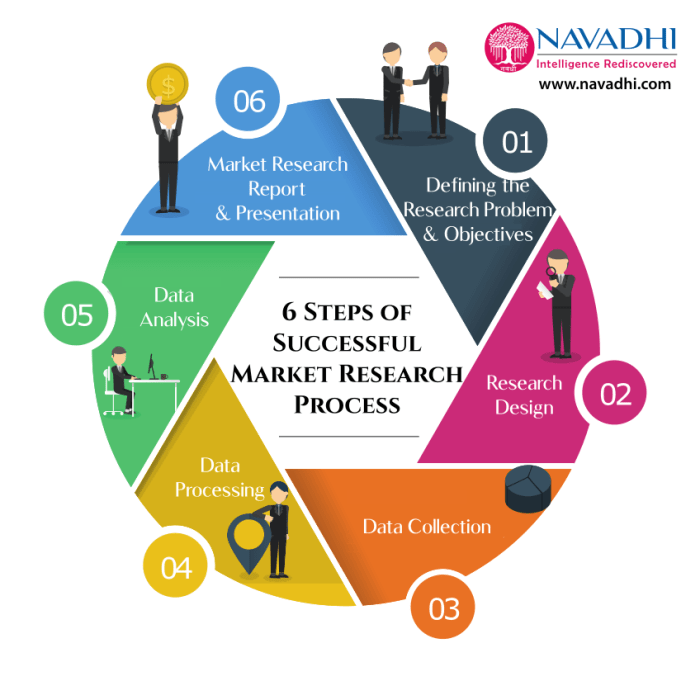
Reporting and Presenting Research Findings: Building A Marketing Research Process
When it comes to reporting and presenting research findings, it is crucial to effectively communicate the results to stakeholders in a clear and concise manner. This ensures that the findings are understood and can be used to make informed decisions moving forward.
Creating Visually Engaging Reports and Presentations
To create visually engaging reports and presentations, consider using charts, graphs, and visuals to help convey the data in a more digestible format. Utilize color coding, infographics, and relevant images to make the information more appealing and easier to comprehend.
- Use bullet points and numbered lists to highlight key findings and recommendations.
- Include visuals such as pie charts, bar graphs, and tables to illustrate data effectively.
- Utilize a consistent design theme and layout to maintain a professional look throughout the report or presentation.
Importance of Clear and Concise Communication
Clear and concise communication of research findings is essential to ensure that stakeholders grasp the implications and insights derived from the study. It helps in avoiding misinterpretations and enables decision-makers to act based on accurate information.
Remember, simplicity is key when conveying complex data. Use plain language and avoid jargon to make the findings easily understandable to a wider audience.