Understanding Sales Cycles dives deep into the rhythm of business transactions, exploring the ins and outs of sales strategies with a fresh perspective that resonates with the high school hip crowd.
Get ready to ride the wave of sales cycles as we break down the key stages and factors that influence this crucial aspect of business success.
Definition of Sales Cycles
Sales cycles are the series of stages that a customer goes through before making a purchase, from initial awareness to final decision. Understanding these cycles is crucial for businesses to effectively target and engage potential customers.
Types of Sales Cycles
- Short Sales Cycle: Typically found in industries with lower-priced products or services, where customers make quick decisions.
- Long Sales Cycle: Common in industries with high-priced or complex products, requiring more time and interaction to close a sale.
- Recurring Sales Cycle: Involves customers who make repeat purchases regularly, such as subscription-based services.
Importance of Understanding Sales Cycles for Businesses
- Targeted Marketing: Helps businesses tailor their marketing strategies to align with different stages of the sales cycle, increasing effectiveness.
- Forecasting Sales: By analyzing sales cycles, businesses can predict future sales trends and adjust their strategies accordingly.
- Improving Customer Relationships: Understanding sales cycles allows businesses to build stronger relationships with customers by providing relevant information at each stage.
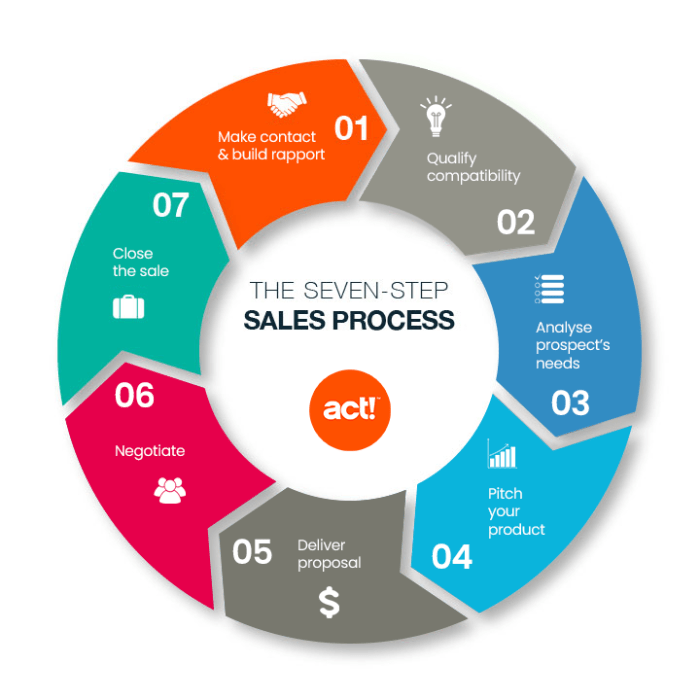
Stages of Sales Cycles
In a typical sales cycle, there are several stages that a potential customer goes through before making a purchase. Each stage involves specific activities that help move the prospect closer to becoming a customer.
1. Prospecting
During the prospecting stage, sales representatives identify potential customers who may be interested in the product or service. This involves researching and reaching out to leads through various channels such as cold calling, email campaigns, and networking events.
2. Qualification
Once leads have been identified, the qualification stage involves determining if the prospect has the budget, authority, need, and timeline (BANT) to make a purchase. This is crucial in ensuring that sales efforts are focused on leads with a higher likelihood of converting.
3. Presentation
In the presentation stage, the sales team presents the product or service to the qualified prospect. This may involve product demonstrations, providing case studies, and addressing any objections or concerns the prospect may have.
4. Closing, Understanding Sales Cycles
The closing stage is where the actual sale takes place. This involves finalizing the terms of the agreement, negotiating pricing, and getting the prospect to commit to making a purchase. Sales representatives use closing techniques to seal the deal.
5. Follow-up
After the sale has been made, the follow-up stage involves nurturing the relationship with the customer. This includes providing support, gathering feedback, and looking for opportunities for upselling or cross-selling.
Short Sales Cycles vs. Long Sales Cycles
Short sales cycles typically involve lower-priced products or services, quick decision-making processes, and a shorter time frame from prospecting to closing. On the other hand, long sales cycles are common in industries with high-ticket items, complex buying processes, and multiple stakeholders involved. Short sales cycles are more transactional, while long sales cycles require relationship-building and strategic nurturing of leads.
Factors Influencing Sales Cycles

Market trends and customer behavior play a crucial role in shaping the length and effectiveness of sales cycles. External factors can also have a significant impact on how sales cycles unfold.
Market Trends Impact on Sales Cycles
Market trends such as economic conditions, industry shifts, and technological advancements can directly influence the length of sales cycles. For example, during a recession, businesses may delay purchasing decisions, leading to longer sales cycles as companies become more cautious with their spending. On the other hand, an industry-wide adoption of a new technology may accelerate sales cycles as companies rush to upgrade their systems to stay competitive.
Customer Behavior in Sales Cycles
Customer behavior, including preferences, needs, and buying habits, can greatly shape sales cycles. Understanding how customers research, evaluate, and make purchasing decisions is essential for businesses to tailor their sales strategies accordingly. For instance, if customers prefer personalized interactions and in-depth product demonstrations, sales cycles may be longer to accommodate these preferences.
External Factors Influencing Sales Cycles
External factors such as regulatory changes, competitive landscape, and global events can impact sales cycles. For example, a new regulation that affects the use of certain products may prompt companies to reevaluate their purchases, leading to longer sales cycles as they navigate compliance issues. Similarly, increased competition in the market can intensify the need for businesses to differentiate themselves, potentially prolonging sales cycles as companies strive to stand out.
Strategies for Managing Sales Cycles
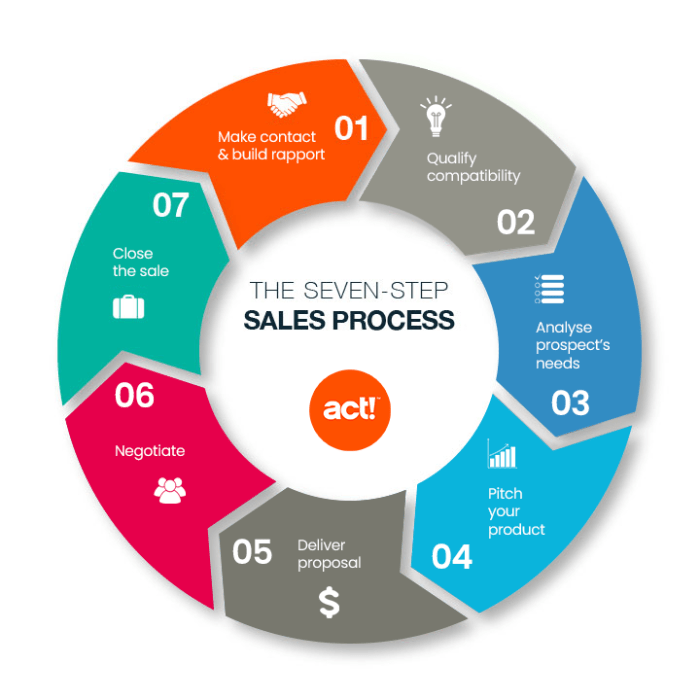
Effective management of sales cycles is crucial for maximizing revenue and ensuring a smooth sales process. By implementing strategic approaches at each stage of the sales cycle, businesses can improve efficiency and drive better results. Customer relationship management plays a key role in nurturing leads and converting them into loyal customers. Accelerating sales cycles without compromising quality requires a balance between speed and personalized service.
Optimizing Each Stage of the Sales Cycle
- Identify target audience: Tailor your sales approach based on the specific needs and preferences of your target customers.
- Qualify leads effectively: Focus on high-quality leads that are more likely to convert into paying customers.
- Personalize communication: Build strong relationships with prospects by offering personalized solutions and addressing their pain points.
- Provide timely follow-ups: Stay engaged with leads throughout the sales process to maintain interest and address any concerns promptly.
Importance of Customer Relationship Management
Customer relationship management (CRM) is essential for building long-term relationships with customers and maximizing lifetime value. By maintaining open communication, addressing customer needs, and providing exceptional service, businesses can enhance customer loyalty and drive repeat sales. CRM tools can help streamline customer interactions and track customer data for more personalized engagement.
Accelerating Sales Cycles
- Streamline processes: Identify and eliminate bottlenecks in the sales cycle to reduce unnecessary delays.
- Offer incentives: Encourage quick decision-making by providing limited-time offers or discounts to motivate prospects to act.
- Utilize technology: Leverage automation tools and data analytics to streamline sales processes and identify opportunities for optimization.
- Empower sales team: Provide training and resources to empower your sales team to efficiently move prospects through the sales cycle.
Case Studies on Sales Cycles: Understanding Sales Cycles
Case studies provide valuable insights into how different companies have successfully managed their sales cycles in various industries. By analyzing these real-life examples, we can learn important lessons on adapting to changing market conditions and improving sales cycle efficiency.
Case Study 1: Software Industry
In the software industry, Company X implemented a proactive approach to their sales cycle by leveraging data analytics to identify potential leads. By analyzing customer behavior and preferences, they were able to tailor their sales strategies effectively, resulting in a significant increase in sales conversions.
“Data-driven decision-making played a crucial role in optimizing our sales cycle and enhancing customer engagement,” said the CEO of Company X.
Case Study 2: Retail Industry
Company Y in the retail sector adapted their sales cycle by integrating an omni-channel approach to reach customers through multiple touchpoints. By combining online platforms, social media, and physical stores, they created a seamless shopping experience that boosted customer loyalty and sales revenue.
“Our multi-channel sales strategy allowed us to connect with customers wherever they are, driving sales growth and brand visibility,” stated the Marketing Director of Company Y.
Case Study 3: Manufacturing Industry
Company Z in the manufacturing sector optimized their sales cycle by implementing a customer relationship management (CRM) system to track interactions and streamline communication with clients. This personalized approach enhanced customer satisfaction and retention, ultimately leading to a higher conversion rate and increased sales.
“By centralizing customer data and improving communication processes, we were able to provide tailored solutions that met our clients’ needs, resulting in improved sales performance,” explained the Sales Manager of Company Z.